ARCH 3020: Design II
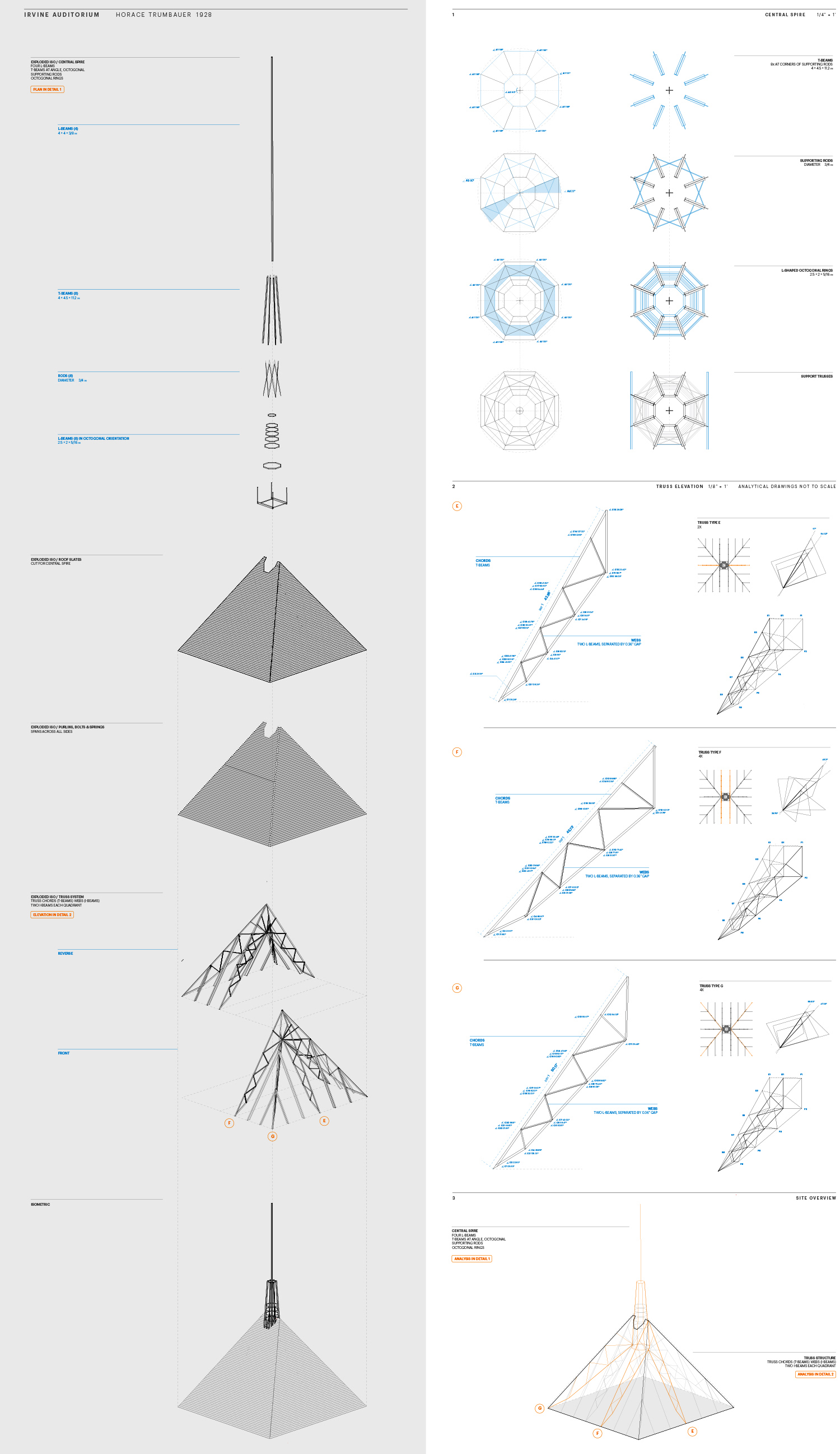
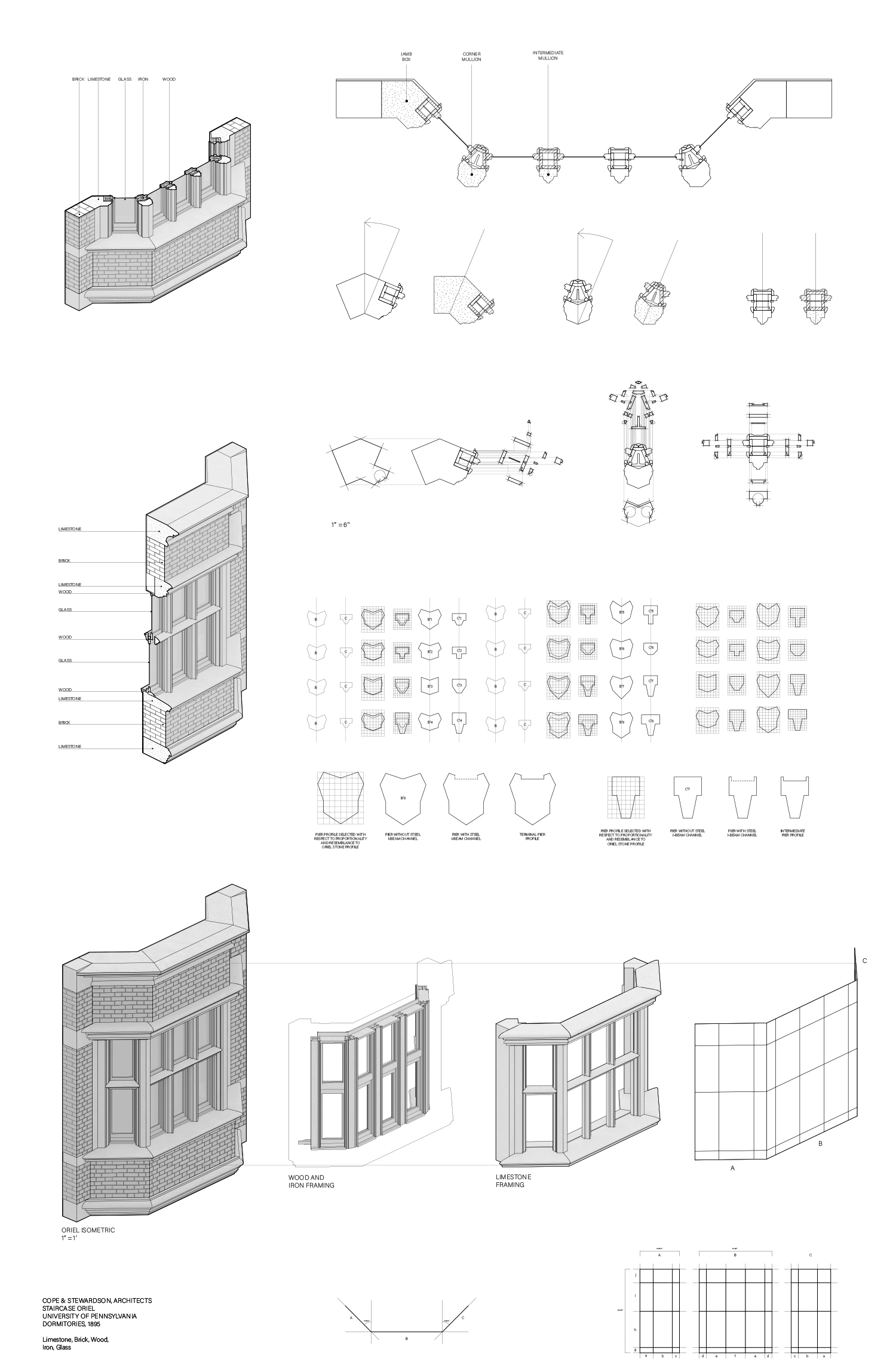
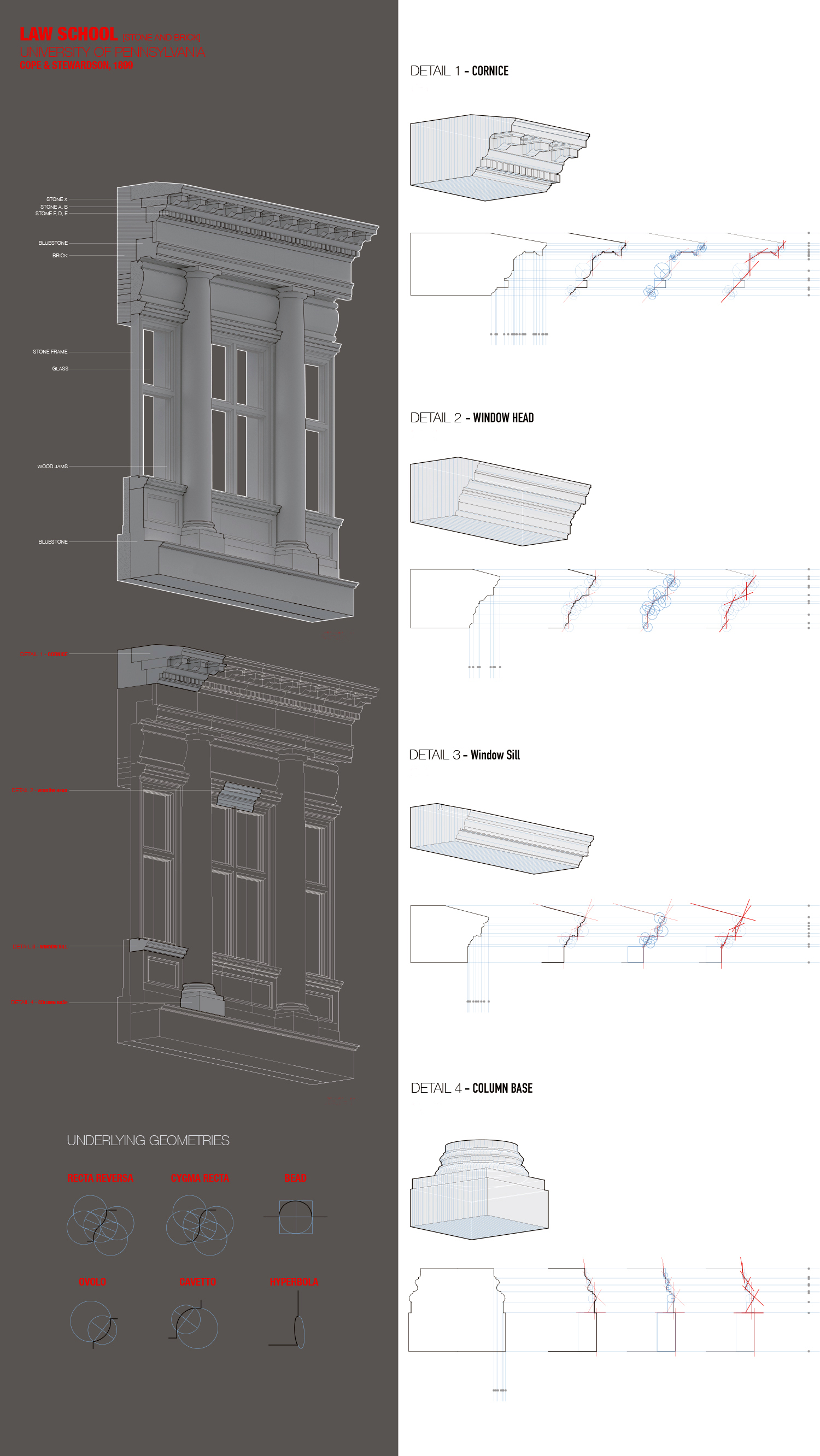
Descriptive geometry is a method to study and project three-dimensional physical space and form working with two-dimensional planes. Also known as constructive geometry, descriptive geometry utilizes analytical and generative sequential operations. In constructive geometry analysis can be understood as design in reverse and design as analysis in reverse.
In the first part of the exercise students analyze the geometry and construction of historical building elements in late-19th and early-20th century buildings on the campus of the University of Pennsylvania: Fisher Hassenfeld College House (Cope & Stewardson, 1895), Law School (Cope & Stewardson, 1898), the Museum (Stewardson & Page, et al., 1912), and Irvine Auditorium (Horace Trumbauer, 1926).
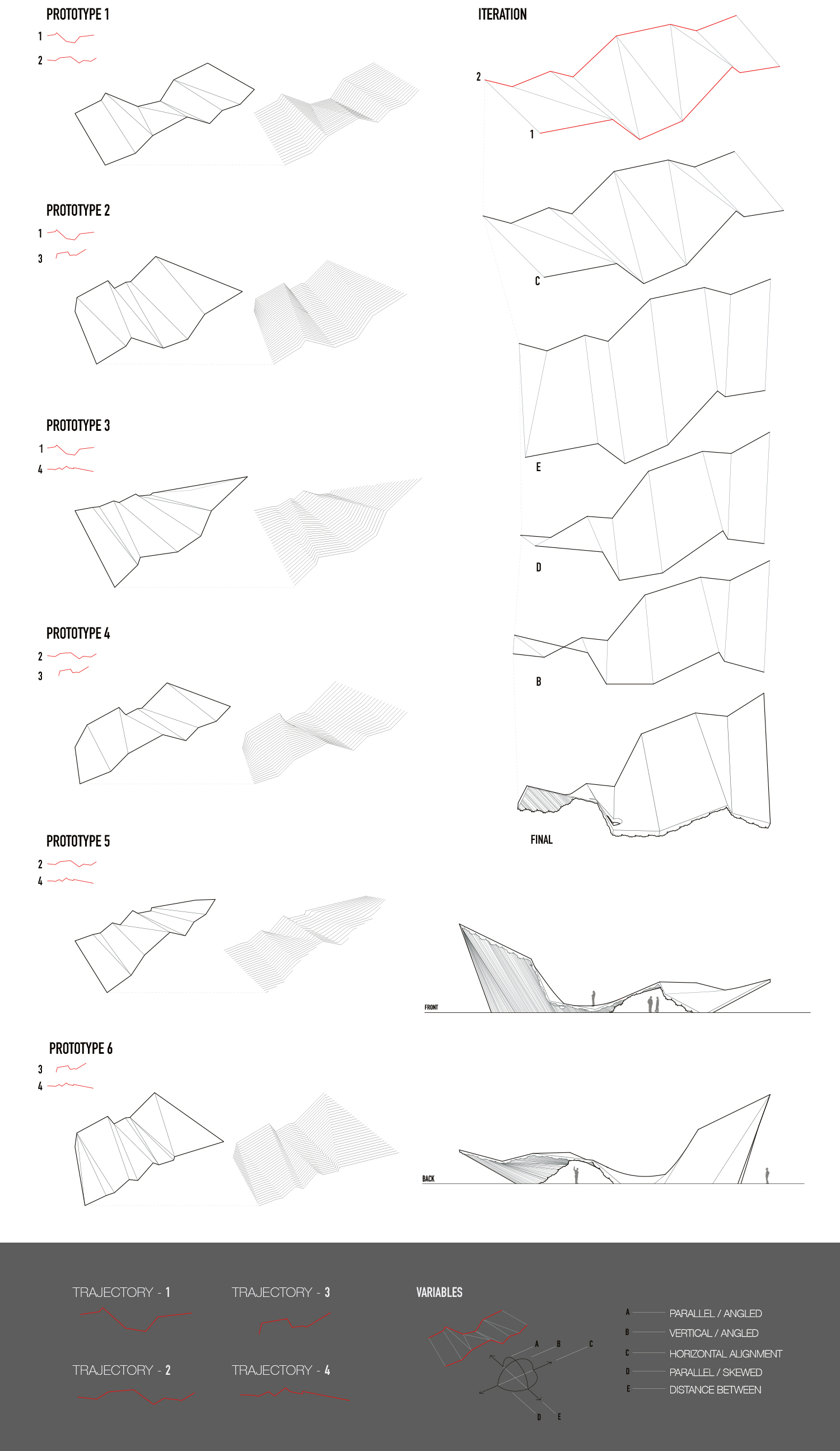
In the second part of the exercise these analytical studies provide the points of departure for the generation of architectural prototypes utilizing descriptive and sequential operations.